MA 249 / ANALYSIS OF FUMONISINS FB1, FB2 AND FB3
USING HPLC WITH POST-COLUMN DERIVATIZATION
INTRODUCTION
Fumonisins are a group of naturally occurring Mycotoxins produced by Fusarium moniliforme fungi species that grow on corn and other commodities. Fumonisins are suspected human carcinogens and are toxic to pigs, poultry and horses. Environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, affect the occurrence of Mycotoxins and contamination can happen in the field as well as during storage. Many countries set limits on the presence of Fumonisins in foods and feeds and testing of raw crops as well as finished products is done on a regular basis.
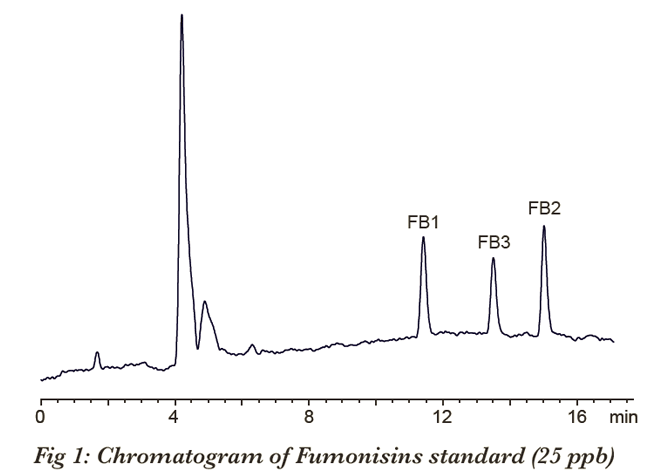
A simple and sensitive method to detect Fumonisins involves using an HPLC to separate the toxins and then converting them using post-column derivatization with OPA into highly fluorescent derivatives.
METHOD
Analytical Conditions
Column: MycotoxTM reversed-phase C18, 4.6 x 250 mm,
Catalog Number 1612124
Temperature: 65 ºC
Flow Rate: 0.8 mL/min
Mobile Phase: Formic acid solution (1 mL formic acid in
1000 mL D.I. water) : MeOH.
See HPLC Program table
Post-Column Conditions
Post-Column System: Pinnacle PCX
Reactor Volume: 1.4 mL
Reactor Temperature: 65 °C
Flow Rate: 0.4 mL/min
Reagent: 300 mg o-Phthalaldehyde, 2g Thiofluor and 3 mL
of 30% Brij 35 solution in 950 mL OD104 Diluent
Detection: FLD detector, λEX=335 nm, λEM=440 nm
Injection Volume: 10-50 uL
HPLC GRADIENT
|
TIME (Min) |
Formic Acid Solution, % |
Methanol, % |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
45 |
55 |
|
2 |
45 | 55 |
|
9 |
30 | 70 |
|
14 |
10 | 90 |
|
16 |
10 | 90 |
| 16.1 | 45 | 55 |
| 23 | 45 | 55 |